When it comes to electrical testing on critical power systems, or performance testing in environments where the risk of liability is high, test data accuracy and results verification is of the upmost importance. Manufacturers, installers, quality control, and equipment owners all have a shared interest in making sure their part of the construction process was done correctly and without error in the event of some conflict or unexpected catastrophe.
For liability and litigation, such as the failure of an apparatus under test or electrical fault upon re-energization, test reports can hold a wealth of information but are easily changed without the proper oversight in place. On extremely high pace construction projects, test reports often get passed around before testing is completed, leading to a confusing paper trail between testing companies, contractors, and commissioning agents.
Building Trust with Distributed Ledger Technology
Blockchains are decentralized networks that offer a system in which transactional records are cryptographically stored and maintained across several computers and linked peer-to-peer. Each computer (node) in the network holds a complete record of each transaction, creating a virtually indestructible database that no single party can control.
Unlike a typical database where information is stored in tables, blockchains store information in “blocks” of data that are strung together. When a data block gets filled, it is set in stone and becomes a part of the network timeline. Each block in the chain is given a unique identifier and timestamped when it is added to the chain.
Not only is the transaction data non-reversible, it is cryptographically linked and immune to any form of tampering. This is what makes distributed ledger technology highly effective against counterfeiting and document fraud. By securing a data over blockchain, you can capture, archive, sign, and prove the exact contents of a file and the exact time it was confirmed.
Because these networks are decentralized, all transactions can be transparently viewed by either having a personal blockchain network node or by using blockchain explorers that allow anyone to see transactions occurring live. The one major limitation of these networks are the transaction speed and storage size of each block.
Verification of Data with Secure Hashing Algorithms
The Bitcoin network, for example, is regarded as one of the most decentralized and secure networks but has a block time of 10 minutes and a block size of just 1MB, hardly enough to store the entire contents of a large document. You can get around this problem by hashing the data (creating a unique id code based on the contents of the file) into a small, shareable text string that is only a few KB in size.
If a single bit of data is ever changed in the original file, its corresponding encryption hash will also change; You can think of it as a digital fingerprint. This is a core benefit that secure hashing algorithms provide.
Hash values provide the best balance because they are far smaller than whole documents and thus a more efficient storage method for blockchain networks. Regardless of where the document is stored, you can verify the contents have not been tampered with by rehashing it and comparing it to the blockchain-stored hash.
For storing multiple documents, the hashes can be placed into a distributed hash table, which can then be stored on-chain. Once you store a hash on the blockchain, it will be there permanently. There is no way to change data once you include it in a block.
How Electrical Testing Data is Secured via Blockchain Networks
Araium is utilizing encryption hash technology as part of its Distributed Test Ledger (DTL) system to reduce risk, enhance efficiency, and maintain transparency between all parties involved. Our file validation tool can be used to secure nearly any external CSV or raw data file from popular testing software such as PowerDB and Doble Test Assistant.
This standalone tool serves as a free utility to anyone who wants to use it and helps to demonstrate how part of the Distributed Test Ledger data validation system operates. Our centralized hybrid service utilizes the same process to store and cryptographically verify highly sensitive and mission critical reports.
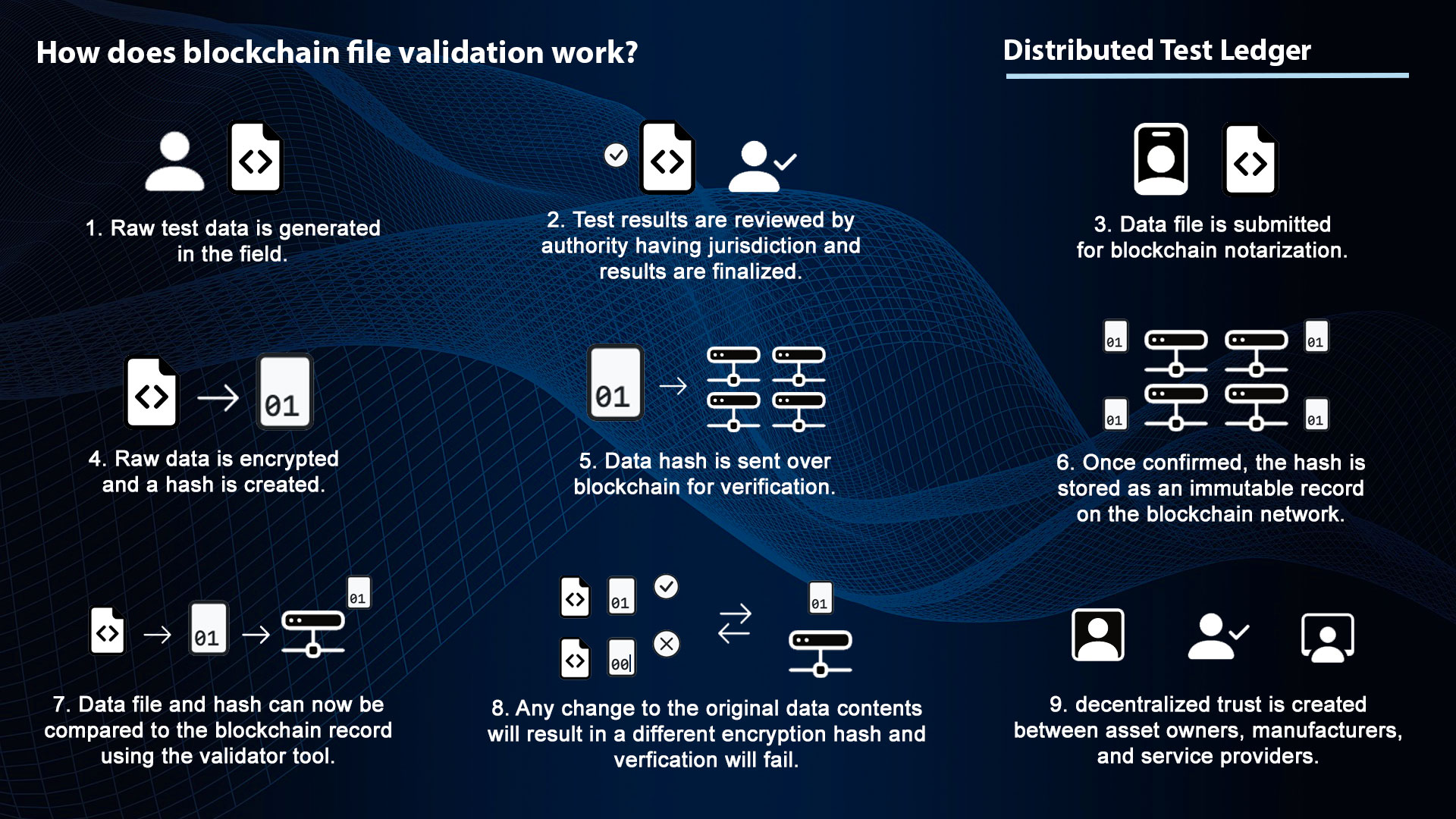
Raw test data is generated by test technicians in the field and sent to the project manager who will work with the authority having jurisdiction for final review. Once all parties are in agreement that the results are accurate, the data file is submitted for notarization on the blockchain.
An encryption hash is created from the original file contents and stored in a transaction over a distributed ledger. Once confirmed by the network, the hash is kept on the blockchain a record on the blockchain that can never be changed.
Transaction reports are provided by Araium for anyone with a copy of the original file and corresponding transaction hash. Any change made to the original file, or comparing a hash to the wrong file, will result in a failed verification. Decentralized trust is created between asset owners, manufacturers, and service providers.
Related
Mitsubishi Electric admits to faking test data on transformers
